Thought Matters, an idea exchange for the highly opinionated, published an excerpt of Hot, Hungry Planet yesterday.
Here’s how the chapter on California and Syria: A Tale of Two Droughts begins:
In the late spring of 2014, while covering food sustainability at the Monterey Bay Aquarium’s Sustainable Foods Institute, I took a trip to the Carmel Valley farm stand run by Earth-bound Farm. Earthbound Farm is the largest organic farming operation in the United States. It cultivates about 50,000 acres of produce, and I spent the morning walking in a small demonstration garden that was nothing short of paradise. Everything was a verdant green. Yet just beyond the farm, where the Carmel Mountains meet the horizon, was dry scrub and pale brown grass, a truer reflection of this parched land. The Golden State, which got its name from the grasses that turn a shade of palomino blond in summer, then green up again during the fall and spring rains, was looking more like the Brown State.
As California’s drought dragged into the next year, I couldn’t shake the sense of a crisis brewing in Carmel Valley. I was also hearing reports of conflict over water in war-torn Syria. I wondered, could water conflict on that scale ever occur here? I couldn’t blame Earthbound’s owners for choosing this idyllic spot, or other farmers for choosing any other location along California’s central coast, where morning fog moistens the otherwise dry landscape. When the founders of the farm first started growing raspberries on two and a half acres, they didn’t imagine it would expand to become America’s largest organic producer of salad greens and vegetables. But Earthbound’s growth was only one among the more recent in decades of farming expansion all across California, and especially the nearby Central Valley, since the Dust Bowl of the 1930s. Through the magic of irrigation, these farmers had made a desert bloom.
While Earthbound’s leafy expanse appeared intact, agriculture is in jeopardy throughout California and other western states. A 2015 investigation in ProPublica reported that California’s drought is part of a much bigger water crisis that is killing the Colorado River, “the victim of legally sanctioned overuse, the relentless forces of urban growth, willful ignorance among policymakers, and a misplaced confidence in human ingenuity.” Climate change will only exacerbate the problem.
Continue reading on Thought Matters and to buy your copy of Hot, Hungry Planet, please go here.













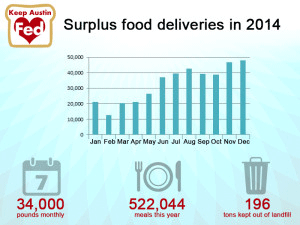 That’s Russell Cavin of Keep Austin Fed, a Texas not-for-profit that rescues nutritious, edible food, and delivers it to local Austin charities. In a county where almost one in five people do not know where their next meal is coming from, Cavin says food rescue makes sense. The food comes from supermarkets and restaurants, which often toss perfectly good fare that looks less than perfect – like a pre-made sandwich with wilted lettuce.
That’s Russell Cavin of Keep Austin Fed, a Texas not-for-profit that rescues nutritious, edible food, and delivers it to local Austin charities. In a county where almost one in five people do not know where their next meal is coming from, Cavin says food rescue makes sense. The food comes from supermarkets and restaurants, which often toss perfectly good fare that looks less than perfect – like a pre-made sandwich with wilted lettuce.



