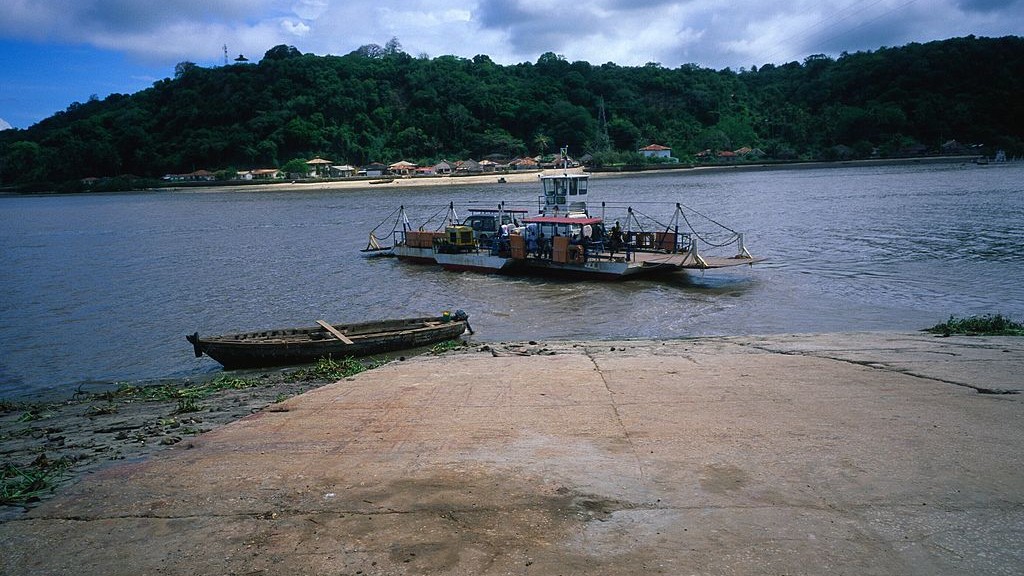
 The Pangani River in Tanzania is important for many reasons: its three major dams provide 17 percent of the country’s electricity; it sustains thousands of farmers and herders living in the basin; and its flow of fresh water supports humans, industry, and ecosystems. But most interesting might be the innovative water policies that govern withdrawals, infrastructure projects, and ecosystems along its banks.
The Pangani River in Tanzania is important for many reasons: its three major dams provide 17 percent of the country’s electricity; it sustains thousands of farmers and herders living in the basin; and its flow of fresh water supports humans, industry, and ecosystems. But most interesting might be the innovative water policies that govern withdrawals, infrastructure projects, and ecosystems along its banks.
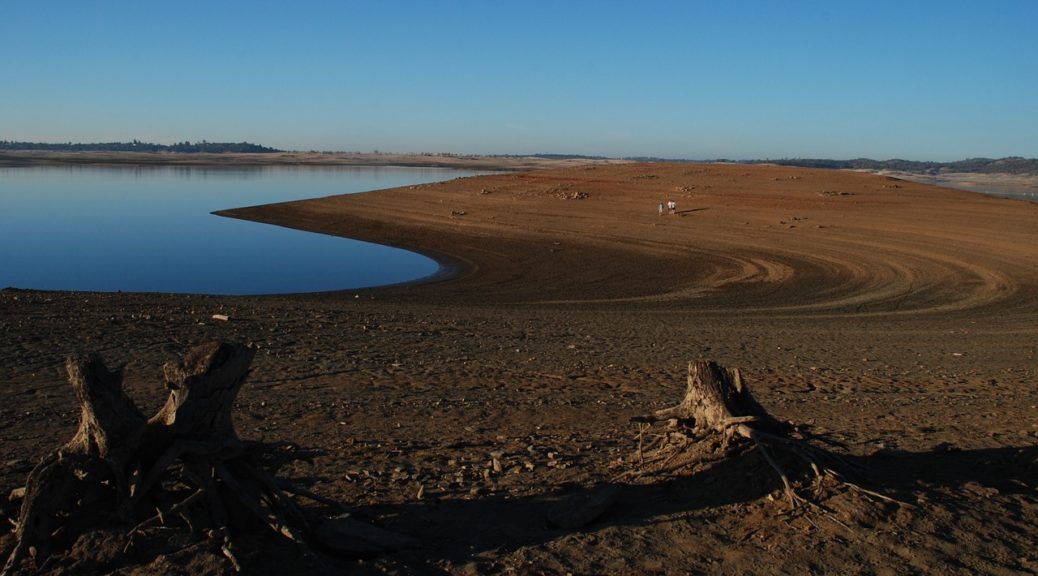
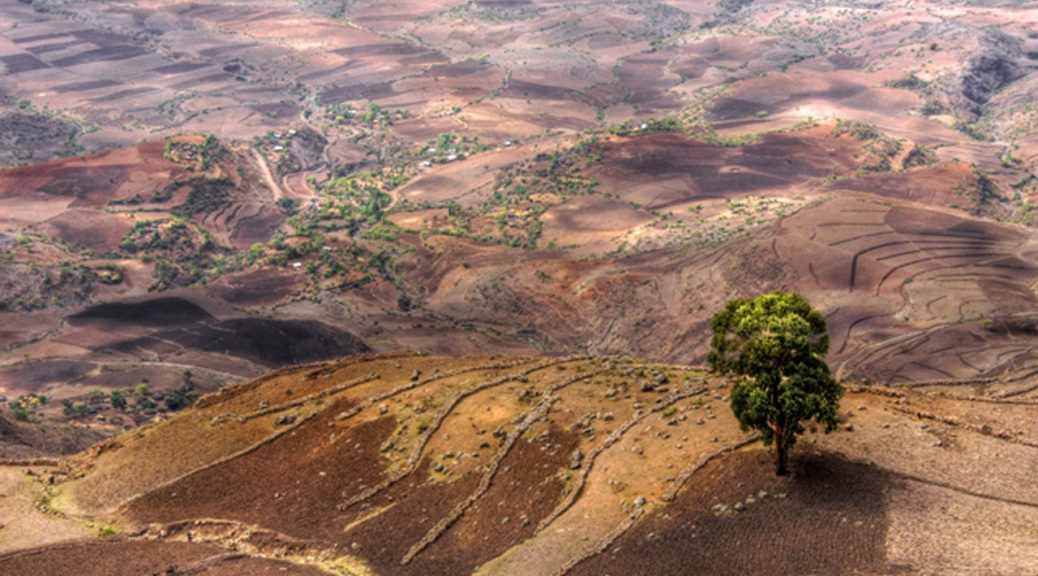
Climate change and population dynamics could cause trouble for the Pangani Basin and many others like it. More people are expected to depend on the flow of fresh water while at the same time rainfall and glacial meltwater from Mt. Meru, Mt. Pare, and Mt. Kilimanjaro are diminishing.
Around the world, water managers are adjusting to a similar quandary. Precipitation patterns and river flows are becoming more uncertain as the past is no longer a reliable guide for the future. Planners are adjusting to changes in the water cycle by integrating policies with flexible structures and ecosystems.
Flexibility Over Scale
In the November 2014 issue of Nature Climate Change, I wrote about how leaders in sustainable water management are finding common ground with two historically antagonistic approaches: engineering and ecology.
I talked with Mark Fletcher, a water engineer and the water business leader at UK-based Arup, a global company of consulting engineers with 14,000 employees. Modular is one way to describe his brand of sustainable water work.
“We had assumed that the world was static,” Fletcher told me. “We knew that the climate was predictable. Due to climate change or due to a changing climate, it is harder to predict things. So rather than build overly conservative monolithic solutions, we now design systems that can be tweaked and twiddled.”
A good example is osmosis desalination. “You literally stack desalination units, much like you would batteries, until you solve your problem,” he said.
From Fletcher’s perspective, the world has no need for more Hoover Dams, given the uncertainty around the global water cycle of the future. I write:
Fletcher favors natural solutions. In New York City, for example, new plans for city orchards and 9,000 grassed bio-swales, which resemble marshy depressions in the land, will slow the flow of storm water from sidewalks to water catchment basins. “Think of them as green sponges all over the city. The water gets soaked up and you avoid pumping every time it rains,” he says. “It’s the gift that keeps on giving.” Furthermore, rather than design water treatment plants that can accommodate extreme rainfall, he prefers multiple local responses that can be changed and adapted, much in the way that a Lego building block is removed and added.
Fletcher suggests that the solution to water management under climate change is beyond engineering. That’s why ecologists John Matthews, coordinator of the Alliance for Global Water Adaptation, and LeRoy Poff, a professor at Colorado State University, have been leading a team of 27 researchers at the U.S. National Socio-Environmental Synthesis Center in Maryland. The team includes economists, hydrologists, policymakers, and engineers. Climate change, they say, has prompted the researchers to work together on an integrated approach to freshwater adaptation. Rather than isolating water management issues within a single field, such as engineering or hydrology, the team’s multifaceted work is developing solutions for decision-makers. Think of their combined work as a chemical reaction. Instead of one element, such as engineering, working in seclusion on a freshwater adaptation project, their form of synthesis science means suddenly more ingredients are added to the beaker.
The research team that Matthews and Poff lead identifies markers of resilience of both infrastructure and ecosystems in basins. They are using the analysis so that ecological principles are incorporated into future water management projects from the very beginning.
Resilience markers include variation of flow, seasonal and temperature changes, and connections to flood plains, for instance. The specific indicators vary from river to river, but the principles remain the same.
Matthews says that the Dujiangyan system in China’s Sichuan Province is a model for integrating policies with engineering and ecology in a sustainable way. Built in 256 BC, the water diversion system still operates today.
According to Kathleen Dominique, an environmental economist at OECD, flexible approaches are necessary to adjust to changing conditions at low cost.
For the Pangani Basin, leaders have established ecosystems as a priority, keeping river flow available to wetlands, riparian forests, and mangroves, and the plan is to adjust water policies with the changing needs of communities. Similarly, the European Union’s water directive is now adjusted every six years to examine all changes and uses of rivers, not only those related to climate change.
For a deeper look at how people are working to become more resilient, improve water security, and preserve ecosystems by incorporating ecological principles into water management, read the complete article in Nature Climate Change.

















